Common types of threats for endpoints
Nowadays, organizations store vast amounts of sensitive data and critical operations within both on-premises and cloud environments, rendering them attractive targets for a diverse range of cyber threats. Recognizing and addressing these threats is vital for ensuring data security, operational stability, and overall protection. So let’s find out more about them in this tutorial!
One of the most popular cyber threats is malware. Malware means “malicious software”, is any software intentionally designed to cause damage to a computer, server, client, or computer network. There are many different variations of malware, but the most popular types of malware includes viruses, ransomware and spyware.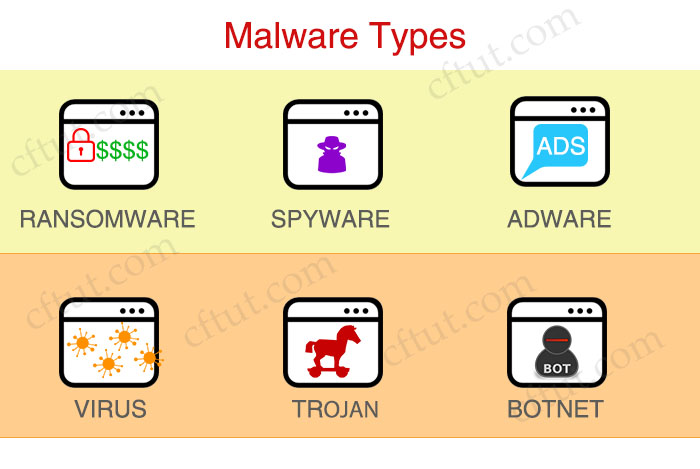
+ Virus is possibly the most common type of malware, viruses attach their malicious code to clean code and wait to be run.
+ Ransomware is malicious software that infects your computer and displays messages demanding a fee to be paid in order for your system to work again. This is usually the scary screen of the victim of this type of attack:
+ Spyware is spying software that can secretly record everything you enter, upload, download, and store on your computers or mobile devices. Spyware always tries to keep itself hidden. Popular types of spyware are keylogger, adware, trojan, rootkit…
++ A keylogger, short for “keystroke logger,” is a type of malicious software or hardware device designed to record and monitor keystrokes typed on a computer or mobile device. The main purpose of a keylogger is to capture sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, personal messages, and other confidential data that a user types on their keyboard. This captured information is then usually sent to the attacker or malicious entity behind the keylogger.
++ Adware is a type of software that displays advertisements to a user while they are using a computer or mobile device. Adware is often bundled with legitimate software or installed without the user’s full awareness, and its primary purpose is to generate revenue for its creators by displaying ads, usually in the form of pop-ups, banners, or other types of online advertisements.
++ A Trojan, also known as a Trojan horse, is a type of malicious software that disguises itself as a legitimate and harmless program or file. Once the Trojan is executed or installed on a computer or device, it carries out malicious actions without the user’s knowledge or consent. Trojans do not replicate themselves like viruses or worms; instead, they rely on the user being tricked into running or installing them.
++ A rootkit is a form of spyware that allows hackers to gain access to and command a computer. The term ‘rootkit’ originally comes from the Unix world, where the word ‘root’ is used to describe a user with the highest possible level of access privileges, similar to an ‘Administrator’ in Windows. The word ‘kit’ refers to the software that grants root-level access to the machine. Put the two together and you get ‘rootkit’, a program that gives someone – with legitimate or malicious intentions – privileged access to a computer. There are four main types of rootkits: Kernel rootkits, User mode rootkits, Bootloader rootkits, Memory rootkits.
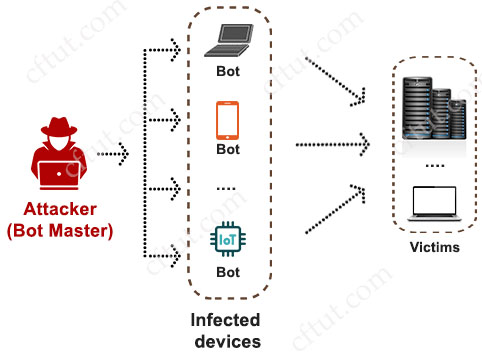
A botnet is a collection of internet-connected devices infected by malware that allow hackers to control them. Cyber criminals use botnets to instigate botnet attacks, which include malicious activities such as credentials leaks, unauthorized access, data theft and DDoS attacks.
An exploit is a code that takes advantage of a software vulnerability or security flaw. An exploit cannot exist without a vulnerability.


